Diet and Nutrition
Vegetarian Diet and Nutrition
A healthy diet is very important
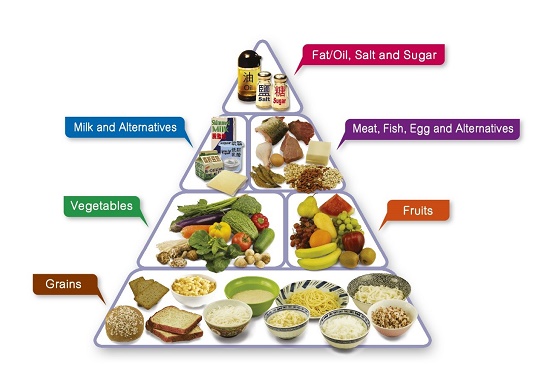
Food is divided into five groups: (1) Grains, (2) Fruits, (3) Vegetables, (4) Meat, Fish, Eggs and alternatives and (5) Milk and alternatives. The nutrients provided by these foods are carbohydrates, protein, fat, minerals and vitamins. Our body obtains different amounts of nutrients from different types of food and then utilises them to promote growth, help development and maintain health. Therefore, in order to obtain sufficient amount of nutrients, we should not be a picky eater.
Eating according to the proportions recommended by “Healthy Eating Food Pyramid” is the key to healthy diet.
What is a vegetarian diet?
- It is a kind of diet that includes mainly fruits, vegetables and grains but excludes all meat. It has become more popular in recent years for the following reasons:
* Some people believe that vegetarian diet is healthier * Some have religious reasons and refrain from eating meat * Some have special beliefs such as environmental protection and animal rights protection * Some people simply want to control their weight and therefore cut down on meat consumption
Types of vegetarian diet
| 1. | Vegan | - Consumes only fruits, vegetables and grains |
| - Does not take dairy products, eggs and meat | ||
| 2. | Lacto-vegetarian | - Consumes only dairy products, fruits, vegetables and grains |
| - Does not take eggs and meat | ||
| 3. | Ovo-vegetarian | - Consumes only eggs, fruits, vegetables and grains |
| - Does not take dairy products and meat | ||
| 4. | Lacto-ovo-vegetarian | - Consumes only dairy products, eggs, fruits, vegetables and grains |
| - Does not take meat |
Examples of vegetarian food
- Grains : red rice, brown rice, white rice, bread, oatmeal
- Nuts and seeds : lotus seed, almond, macadamia nut, hazelnut, brazil nut
- Beans, bean products and legumes : soya bean, lentil, red kidney bean, chicken pea, tofu, peanuts
- Fruits and vegetables : bok choy, lettuce, carrot, tomato, mushroom, pumpkin, cucumber, apple, orange, banana
Benefits of vegetarian diet
- Vegetarian food is rich in dietary fibre, giving a sensation of fullness, which in turn can control food intake and help maintain a normal body weight.
- Decrease the risk of colon cancer, haemorrhoids, constipation, heart disease, hypertension, stroke, cancer and gallstones.
Tips of vegetarian diet for children and youth
A balanced vegetarian diet can support growth during childhood. However, obtaining adequate nutrients (especially protein, vitamin B12 and iron) from vegetarian diet needs more effort when planning the diet so as not to cause malnutrition, anaemia or other diseases.
Puberty is a period of which youths need more energy and nutrients. Some teenagers may not obtain adequate nutrients from breakfast, lunch and dinner. Therefore they should choose nuts, fruits, nutrients fortified plant-based milk and low fat dairy products e.g. milk, cheese, yoghurts etc. as snacks to replace junk foods such as candies, chips, sugary beverages etc. Choosing vegetarian foods carefully can help build healthy eating habits.
In general, vegetarian foods do not have strong taste and are not particularly appetizing. Parents need to put more efforts and be more creative in their cooking by using different spices, vegetarian foods and cooking methods to make different dishes in order to increase children’s interest in food and stimulate their appetite.
Important nutrients for vegetarian children and youth
| Fats |
|
| Protein |
|
| Iron |
|
| Calcium |
|
| Zinc |
|
| Iodine |
|
| Omega-3 fatty acids |
|
| Vitamin B12 |
|
If necessary, please consult your family doctor before purchasing food supplements so as not to affect your health.
(Revised in June 2023)