Bridge
This Newsletter aims to promote communication between students and the Student Health Service of the Department of Health
May 2017 Issue No.73
Published by the Student Health Service, Department of Health
How Much You Know about Fat
Editor’s Note
When we talk about "fat", most of us regard it as a "bad thing" which is hazardous to health. Students planning to keep fit or on diet might be in great fear of "fat". Some of them might even refuse to eat any fat-containing food because they are afraid of weight gain.So, is “fat” good or bad? Coconut oil becomes more popular recently as it is thought that vegetable oil contains more "good fat". Is this true?
In this article, our dietitian will help us understand more about dietary fat so that we can make a wiser choice on healthy eating.
How Much You Know about Fat
Is fat really so bad? How should we choose dietary fat in order to be a smart eater?
Functions of Fat :
- Dietary fat is a concentrated source of energy, each gram of fat provides 9 kcal of energy (one gram of carbohydrate / protein provides 4 kcal of energy)
- Fat carries fat-soluble vitamins (Vitamin A, D, E and K)
- Fat protects organs against shock and prevents heat loss in cold environments
Health Impacts of Excessive Fat Intake
- Excess fat intake can cause obesity
- Increases the risk of heart disease, obesity, hypertension, diabetes and certain types of cancers
How to choose different types of Fats
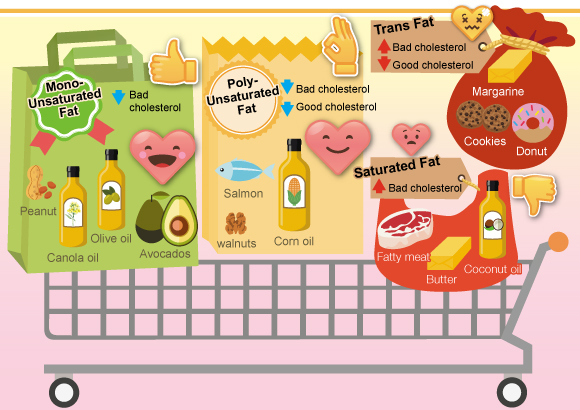
Fats that should be reduced / restricted in intake:
| Intake recommendation | Impact on health | Food source | |
| Saturated fats | Contributes not more than 10% of daily energy intake1 | ↑ bad cholesterol levels ↑ risk of heart disease |
Lard Butter Coconut oil Palm oil |
| Trans fats | Contributes not more than 1% of daily energy intake1 | ↑ bad cholesterol levels ↓ good cholesterol levels ↑↑ risk of heart disease |
Margarine Processed foods made with partially hydrogenated oils (eg. Pastry, chips, biscuits, cake) |
Fats that can be chosen to replace saturated fats and trans fats:
| Intake recommendation | Impact on health | Food source | |
| Polyunsaturated fats | Total fat intake contributes 15%-30% of daily energy intake1 | ↓ good cholesterol levels ↓ bad cholesterol levels |
Sunflower oil Corn oil Mackerel Nuts |
| Monounsaturated fats | ↓ bad cholesterol levels ↓ risk of heart disease |
Olive oil Canola oil Peanut oil Avocados |
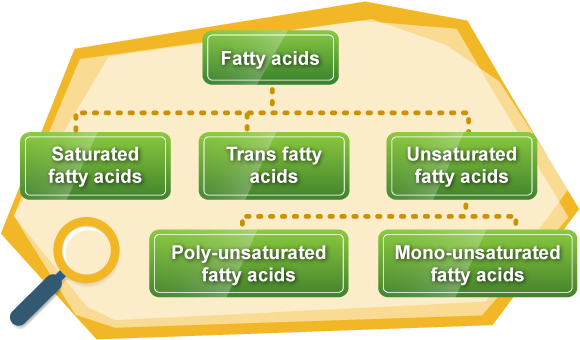
Classification of Fats
Are Plant Fats Healthy?
NO!
The following graph reveals that certain plant fats contain as much saturated fat as animal fats, and among them, coconut oil contains about double the amount of saturated fat found in Lard!
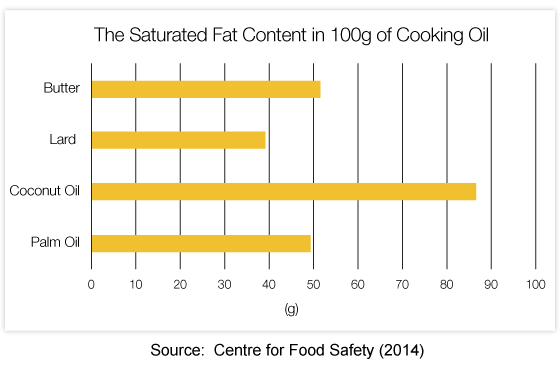
In recent years, coconut oil has been very popular. Lots of advertisements claim that it has plenty of amazing benefits, such as weight loss, blood sugar control and prevention of osteoporosis etc. However, the fact is that coconut oil has around 90% of saturated fat content and the World Health Organization recommends the general public to limit saturated fat intake, including those from coconut oil, to lower the risk of cardiovascular diseases. There is not enough evidence so far to prove the health benefits of coconut oil. Be a smart consumer and do not just take what advertisements say.
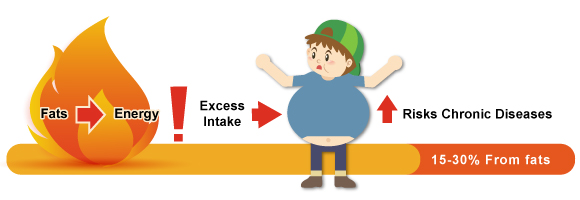
Conclusion
We should not have excess intake of fat, regardless of the type of fats. The daily fat intake should be less than 30% of total energy, saturated fat intake should not exceed 10% and trans-fat intake should not exceed 1% of daily energy intake, so as to avoid obesity and increasing the risks of non-communicable diseases.
References:
| 1. | Centre for Food Safety (2016) < Nutrients Definition and Function > http://www.cfs.gov.hk/tc_chi/nutrient/nutrientc.php |
| 2. | Centre for Food Safety (2014) < Nutrient Information Inquiry > http://www.cfs.gov.hk/english/nutrient/fc-nutrientvalue.php |
| 3. | Health@work.hk project (2014) < Coconut Oil: A Miraculous Oil? > http://www.healthatwork.gov.hk/en/content.asp?MenuID=125 |
| 4. | Health@work.hk project (2014) < “Oil” in Healthful Diet > http://www.healthatwork.gov.hk/en/content.asp?MenuID=158 |
This publication is produced by the Student Health Service, Department of Health.
Tel: 2349 4212 / 3163 4600 Fax: 2348 3968 Web site: www.studenthealth.gov.hk
If you have any comments, you may email to our Edition Board at shsbridge@dh.gov.hk
(Revised in May 2017)