Diet and Nutrition
Obesity and Health
Definition of obesity
Overweight (including obesity) is defined as Body Mass Index (BMI) exceeding 91st percentile line among students of the same sex and age group.
For students who aged 18 years or above, a BMI between 23 and 24.9 indicates overweight. A BMI of 25 or above is obese.
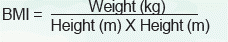
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source: Hong Kong 2020 Growth References
Causes of obesity
| 1. |
Excessive energy (calorie) intake
|
| 2. |
Insufficient energy expenditure, lack of exercise
|
| 3. |
Others e.g. hereditary factors, effects of illnesses or drugs |
Impact of obesity
| 1. |
Physical aspect
|
| 2. |
Social aspect
|
| 3. |
Psychological aspect
|
Prevention of student obesity
|
* | avoid binge eating |
| * | control the desire for food |
|
* | know more about food; understand that being fat does not mean good health or blessing |
| * | adopt healthy eating habits to be a good example to children |
|
* | tuck shop should avoid selling high energy food and drinks, e.g. deep-fried chicken wings, soft drinks |
| * | supply healthy lunch boxes with less meat and oily food |
Essential factors in weight control
- Overweight students and their parents have to acknowledge that it is essential to control weight and set out a weight control plan together
- Adopt a healthy lifestyle and good eating habits in the family. Parents and other family members should strongly encourage children to have determination and confidence in developing good eating habits and increasing exercise level. Do not spoil them and meet all their demands
- Measure students' weight and height regularly in order to increase one's confidence during weight control
- Teach student how to express their emotions appropriately
Weight control tips
| 1. |
Encourage students to follow the Healthy Eating Food Pyramid to eat various kinds of food in the right proportion. Develop a healthy eating habit and avoid picky eating |
| 2. |
Avoid eating too much meat and high sugar or high energy food or drinks including
|
| 3. | Choose lower energy snacks e.g. fruits, cherry tomatoes, skimmed milk, boiled corn, chestnuts |
| 4. |
Cooking tips
|
| 5. |
Eating habits
|
| 6. |
Make lifestyle changes
|
| 7. |
Increase energy expenditure
|
Remember :
- Prevention is better than cure. The risk of developing chronic diseases can be reduced by weight control.
- Place emphasis on long-term weight control and maintenance of good health instead of short-term weight loss. This can be achieved by developing good eating habits and a healthy lifestyle.
(Revised in September 2024)